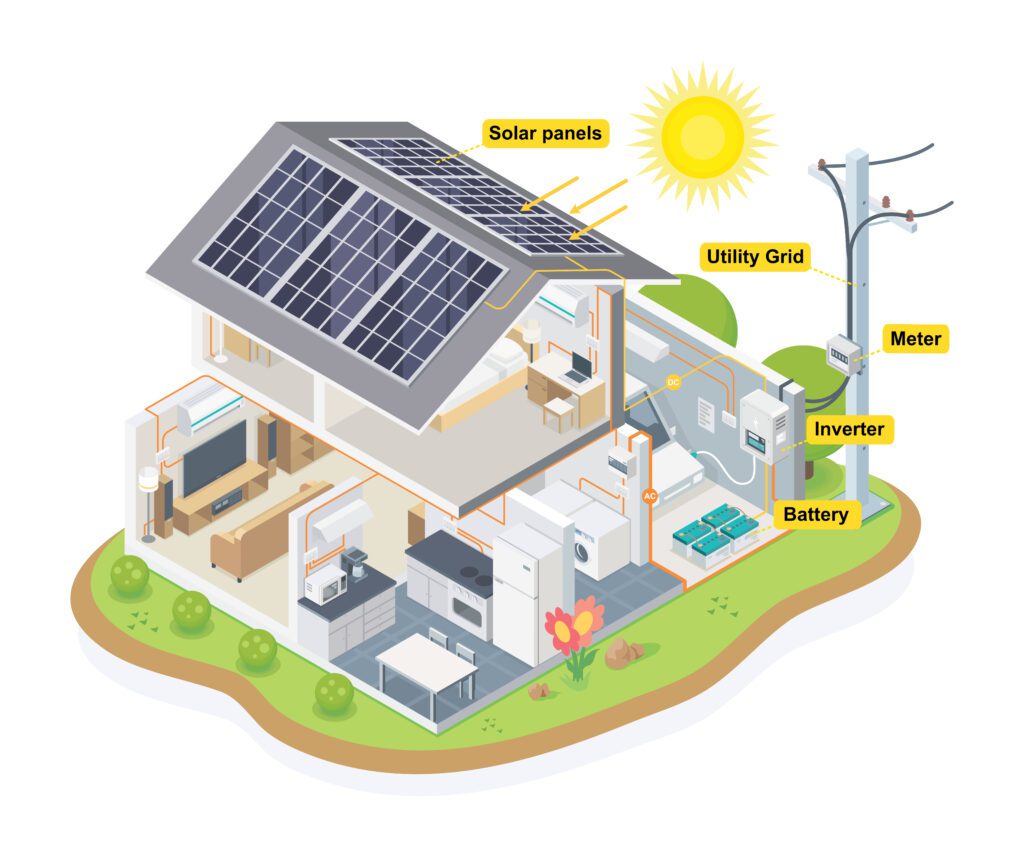
Step 1 – The solar panels capture tiny particles of energy from sunlight, called photons which creates an electrical current or direct current (DC). Yellow wires
Step 2 – The DC current travels through wires to the inverter where the DC current is changed into alternating current (AC) which is what homes and appliances use. Orange wires
Step 3 – The electrical current leaves the inverter and is distributed around the home for use. Any excess energy that is produced can either be stored in your in-home batteries or is routed to a meter and back to the grid or power company (e.g. Rocky Mountain Power).

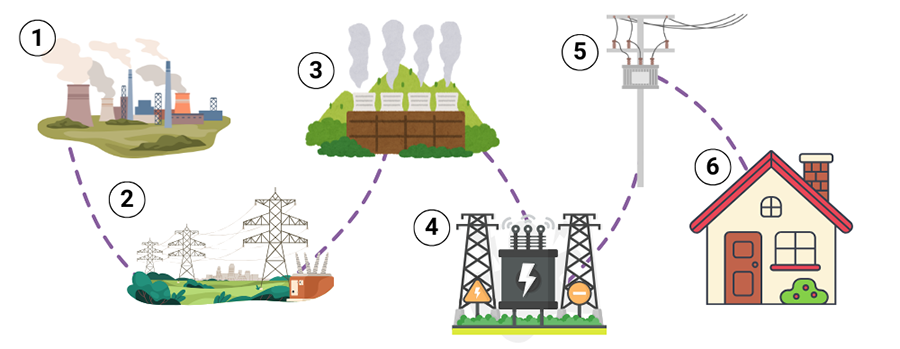
Step 1 | Power Plants- They use energy from fuels like coal, gas, or uranium, or from natural sources like water, wind, or sunlight. In most power plants, fuel is burned to make heat. The heat turns water into steam, and the steam spins a machine called a turbine. The turbine is connected to a generator that makes electricity.
Step 2 | Step-up Transformer & Transition lines– A step-up transformer increases the voltage of electricity, allowing it to travel long distances through transmission lines with less energy loss.
Step 3 | Transmission Substation- A transmission substation is a place where electricity is lowered from high voltage to a safer, lower voltage. It helps move electricity from power lines to homes and businesses.
Step 4 | Distribution Substation- A distribution substation takes electricity from the transmission substation and lowers the voltage even more. It then sends the electricity to homes and businesses through local power lines.
Step 5 | Transformers- Transformers are devices that change the voltage of electricity. They can either increase or decrease the voltage. This helps electricity travel long distances or be used safely in homes and businesses.
Step 6 | Power- A house accepts power from transformers through wires that connect to the home’s electrical panel. The transformer lowers the voltage to a safe level before it enters the house to be distributed via outlets and switches.
Start leveraging clean energy and reducing your power bill today. Learn more about our programs and get a free quote for your home or business.